-
CN
-
Service Hotline
+8618129931046 Mr. Liao


Time:2025-12-25 Views:1
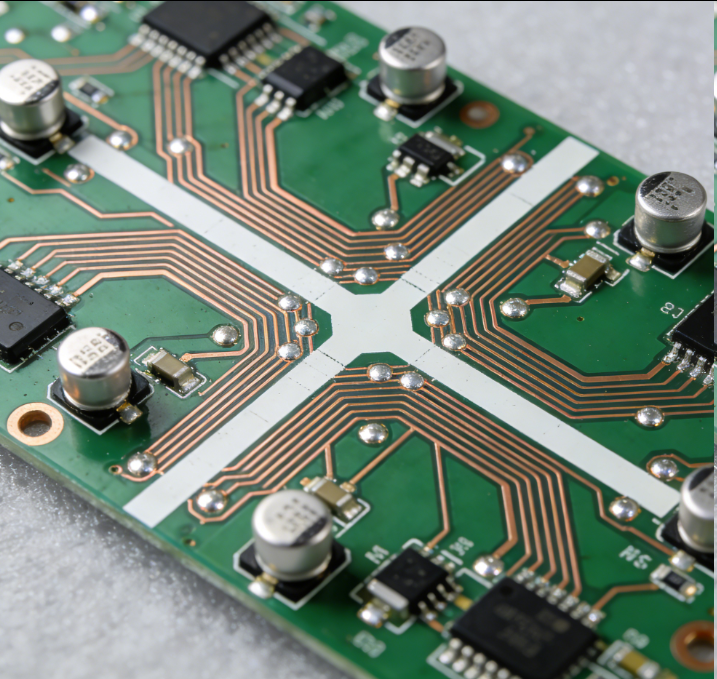
EV PCBs (Electric Vehicle Printed Circuit Boards) are high-performance, durable circuit boards tailored to the unique demands of electric vehicles—powering critical systems like battery management, motor control, infotainment, and ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems). Unlike consumer electronics PCBs (which prioritize miniaturization and low cost), EV PCBs must withstand extreme automotive conditions: wide temperature fluctuations (-40°C to 125°C), high vibration, electromagnetic interference (EMI), and high voltage/current loads (essential for EV powertrains).
The core design of EV PCBs focuses on reliability and performance: they use high-grade materials like FR-4 with enhanced thermal conductivity (to dissipate heat from power-dense components like MOSFETs and microcontrollers) and thick copper layers (2–4 oz vs. 1 oz in consumer PCBs) to handle high current flow without overheating. For example, a battery management system (BMS) PCB in an EV uses multiple copper layers to monitor cell voltage, temperature, and current across hundreds of lithium-ion cells—ensuring safe charging/discharging and preventing thermal runaway. Motor control unit (MCU) PCBs integrate power modules and gate drivers, requiring robust insulation to handle voltages up to 800V (common in modern EVs) and resist EMI that could disrupt other vehicle systems.
Key features of EV PCBs include automotive-grade certifications (e.g., IATF 16949 for quality management) and environmental resilience: they are coated with conformal coatings (e.g., acrylic or silicone) to resist moisture, dust, and chemical exposure (from coolants or road salts). Many also include redundant circuits for safety-critical systems (e.g., ADAS sensors), ensuring functionality even if one circuit fails.
Practical applications span all EV subsystems: BMS PCBs optimize battery life and safety, MCU PCBs control electric motor torque and speed, infotainment PCBs power touchscreens and connectivity features, and ADAS PCBs process data from cameras, radar, and LiDAR. As EVs advance toward higher autonomy and longer range, EV PCBs are evolving to support faster data transfer (via high-speed signal layers) and integration with 5G or V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) communication. For automotive manufacturers, EV PCBs are the backbone of electrification—enabling efficient, safe, and smart vehicle operation that meets strict global emissions and safety standards.