-
CN
-
Service Hotline
+8618129931046 Mr. Liao


Time:2025-09-29 Views:1
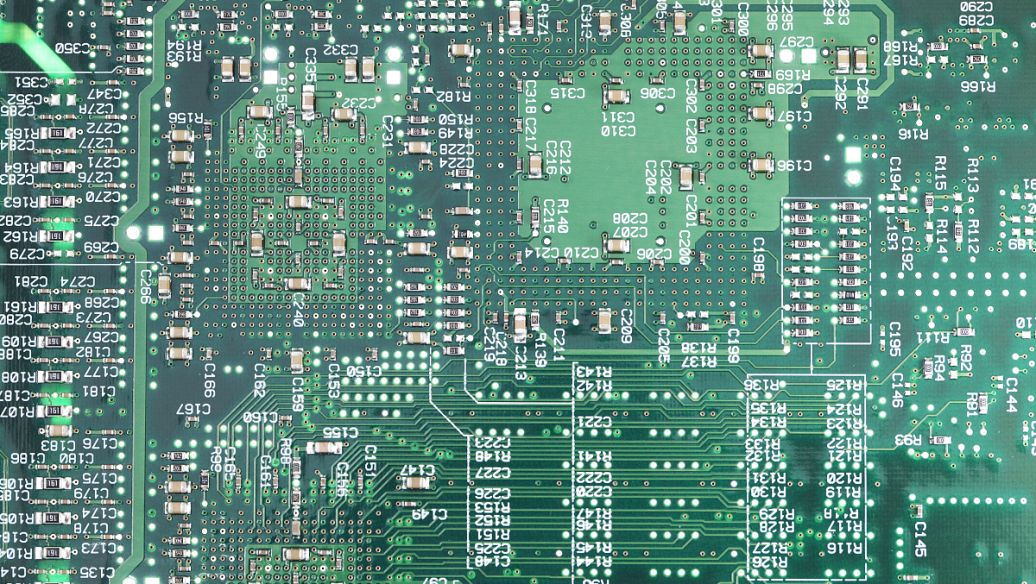
PCB component layout design is a foundational step in printed circuit board development, involving the strategic placement of electronic components to optimize performance, reliability, and manufacturability. This process requires careful consideration of electrical, thermal, and mechanical factors to ensure the PCB functions as intended in its target application.
One of the primary principles of component layout is grouping related components based on their functional roles. For example, analog circuits, digital circuits, and power management components should be separated to minimize interference. High-speed components like microprocessors, oscillators, and transceivers need to be placed close to each other to reduce signal delay and noise, while passive components such as capacitors and resistors should be positioned near the active components they support—decoupling capacitors, for instance, should be placed as close as possible to IC power pins to suppress voltage fluctuations.
Thermal management is another critical aspect. Heat-generating components like power transistors, voltage regulators, and LEDs must be placed to allow efficient heat dissipation. This may involve positioning them near the edges of the PCB for better airflow, using heat sinks, or placing them on thick copper planes to spread heat. Additionally, sensitive components like sensors or analog-to-digital converters should be kept away from heat sources to prevent performance degradation.
Mechanical constraints also influence layout design. Components must fit within the PCB’s physical dimensions and avoid interference with enclosures, connectors, or other mechanical parts. Through-hole components may require alignment with mounting holes, while surface-mount devices (SMDs) need sufficient spacing for soldering and inspection.
Manufacturability considerations include maintaining consistent component spacing, avoiding overly dense placements that complicate assembly, and ensuring that the layout supports automated assembly processes like pick-and-place machines. Adhering to design rules such as minimum trace widths, clearances, and component pitch requirements helps reduce manufacturing errors and costs.
By balancing these factors, PCB component layout design lays the groundwork for a functional, reliable, and cost-effective circuit board.