-
CN
-
Service Hotline
+8618129931046 Mr. Liao


Time:2026-01-13 Views:1
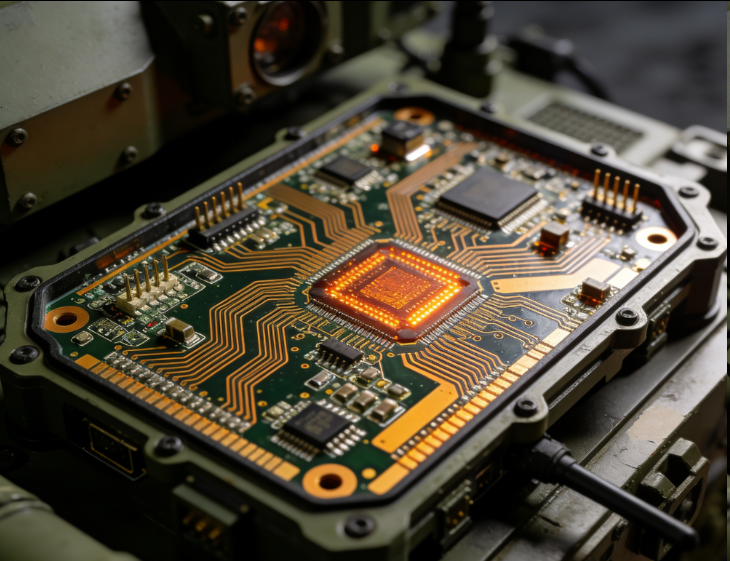
Rigid - flex composite PCB circuit boards represent a revolutionary advancement in printed circuit board technology, combining the benefits of rigid and flexible PCBs to meet the complex requirements of modern electronic devices. These boards integrate rigid sections, which provide structural stability and support for components, with flexible sections that offer flexibility and the ability to bend, fold, or twist. This unique combination enables designers to create compact, lightweight, and highly functional electronic products that can adapt to various form factors and mechanical constraints.
The construction of rigid - flex composite PCBs involves multiple layers of materials. The rigid sections are typically made from traditional printed circuit board materials, such as fiberglass - reinforced epoxy (FR - 4), which offer high mechanical strength, good electrical insulation, and excellent dimensional stability. These sections are used to mount components like integrated circuits, connectors, and passive components, providing a stable platform for reliable electrical connections. On the other hand, the flexible sections are usually composed of polyimide or other flexible polymers, which have excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. These flexible materials are laminated with thin - copper foils to create conductive traces, allowing for the transmission of electrical signals between different parts of the circuit.
One of the key advantages of rigid - flex composite PCBs is their space - saving design. In applications where space is at a premium, such as in aerospace, medical devices, and wearable electronics, these boards can be customized to fit into tight and complex spaces. The flexible sections can be routed through narrow gaps, around obstacles, or folded to reduce the overall footprint of the electronic assembly. For example, in a miniature medical implant, a rigid - flex PCB can be designed to fit the curved shape of the implant while providing a stable platform for the delicate electronic components. This not only saves space but also simplifies the assembly process, as multiple rigid PCBs and cables that would otherwise be required can be replaced by a single rigid - flex board.
Another benefit is improved reliability. By reducing the number of interconnections and cables, rigid - flex composite PCBs minimize the risk of mechanical failures and electrical discontinuities. The integrated design ensures a more robust and stable electrical connection between components, as there are fewer points of potential failure. Additionally, the flexible sections can absorb mechanical stresses and vibrations, protecting the components from damage. In automotive applications, where the electronics are exposed to constant vibrations, rigid - flex PCBs can enhance the durability and lifespan of the electronic systems.
The manufacturing process of rigid - flex composite PCBs is complex and requires advanced techniques. It involves precise lamination, drilling, plating, and etching processes to create the desired circuit patterns on both the rigid and flexible sections. Specialized equipment and expertise are needed to ensure the quality and reliability of the boards. However, with the increasing demand for miniaturized and high - performance electronic devices, the use of rigid - flex composite PCBs is expected to grow, as they offer a versatile and efficient solution for modern circuit design challenges.